Building a Startup Business kicks off the journey to entrepreneurial success, diving into the key components of the startup ecosystem, crafting a solid business plan, securing funding, building a strong team, and developing a Minimum Viable Product (MVP). Get ready to ride the wave of innovation and creativity!
Understanding the Startup Ecosystem
In the world of startups, the ecosystem is a complex network of interconnected elements that play a crucial role in the success of a new business.
Key Components of a Startup Ecosystem
- Entrepreneurs: The driving force behind startups, individuals with innovative ideas and a passion for creating something new.
- Investors: Provide the necessary funding for startups to grow and scale their operations.
- Support Organizations: Accelerators, incubators, and co-working spaces that offer guidance, resources, and mentorship to startups.
- Universities: Sources of talent, research, and innovation that can fuel startup growth.
Role of Accelerators and Incubators
Accelerators and incubators are vital components of the startup ecosystem, providing startups with mentorship, networking opportunities, and access to funding.
Importance of Networking
Networking is essential in the startup community as it allows entrepreneurs to connect with potential partners, investors, and customers, helping them grow their business and gain valuable insights.
Impact of Government Policies
- Government policies can have a significant impact on startup development by creating a favorable environment through tax incentives, grants, and regulations that support innovation and entrepreneurship.
- Regulatory barriers can also hinder startup growth, so it’s essential for governments to create policies that foster a thriving startup ecosystem.
Creating a Business Plan
Creating a business plan is essential for the success of any startup. It serves as a roadmap that Artikels the goals, strategies, and financial projections of the business. A well-thought-out business plan can help attract investors, secure loans, and guide the growth of the company.
Essential Elements of a Startup Business Plan
- Executive Summary: A brief overview of the business, including its mission, product or service offered, target market, and financial highlights.
- Company Description: Detailed information about the business, its history, vision, and goals.
- Market Analysis: Research on the industry, target market, and competitors to identify opportunities and challenges.
- Organization and Management: Structure of the business, key team members, and their roles.
- Product or Service Line: Description of the offerings, their unique features, and benefits to customers.
- Marketing and Sales Strategy: Plans to reach and attract customers, pricing strategy, and sales projections.
- Financial Projections: Revenue forecasts, budget, and cash flow statements.
- Funding Request: Amount of funding needed and how it will be used.
- Appendix: Additional information, such as resumes of key team members, legal documents, and market research data.
Conducting Market Research for a Startup
Market research is crucial for understanding the industry, target market, and competition. It involves gathering and analyzing data to make informed decisions about the business. Methods include surveys, interviews, focus groups, and analyzing industry reports.
Defining a Target Market and Developing a Unique Value Proposition
To define a target market, identify the ideal customers based on demographics, behavior, and needs. A unique value proposition differentiates the business from competitors by highlighting what sets it apart and why customers should choose it.
Examples of Successful Startup Business Models
- Software as a Service (SaaS): Companies like Salesforce and Dropbox offer subscription-based software solutions.
- Marketplace: Platforms like Airbnb and Etsy connect buyers and sellers for various products and services.
- Direct-to-Consumer (DTC): Brands like Warby Parker and Casper sell products directly to customers, bypassing traditional retail channels.
- Freemium: Apps like Spotify and LinkedIn offer basic services for free with premium features available for a subscription fee.
Securing Funding
Securing funding is a crucial step for any startup business looking to grow and expand. There are various sources of funding available, each with its own set of pros and cons. Let’s dive into the different options and how to go about securing funding for your startup.
Sources of Funding
- Bootstrapping: Using personal savings or revenue generated by the business to fund its operations. Pros include maintaining full control and ownership, but cons may include limited resources and slower growth.
- External Investment: Seeking funding from venture capitalists, angel investors, or crowdfunding platforms. Pros include access to larger amounts of capital, but cons may involve giving up equity or control.
- Bank Loans: Traditional loans from financial institutions can provide capital for startups. Pros include lower interest rates, but cons may involve strict repayment terms and requirements.
- Grants: Government or private grants can offer non-dilutive funding for startups. Pros include not giving up equity, but cons may involve stringent eligibility criteria and reporting requirements.
Pitching to Investors
- Prepare a compelling pitch deck outlining your business idea, market opportunity, team, and financial projections.
- Practice your pitch and be ready to answer questions about your business model, competition, and growth strategy.
- Network with potential investors and seek introductions through mutual connections for a warmer introduction.
Alternative Funding Options
- Crowdfunding: Platforms like Kickstarter or Indiegogo allow you to raise funds from a large number of individuals in exchange for rewards or early access to products.
- Contests and Competitions: Participating in startup competitions can provide funding, mentorship, and exposure for your business.
- Corporate Partnerships: Collaborating with established companies can provide funding, resources, and access to new markets.
Building a Strong Team: Building A Startup Business
Building a strong team is crucial for the success of a startup business. A cohesive and talented team can drive innovation, productivity, and growth. Let’s delve into the key aspects of building a strong team for your startup.
Key Roles Needed in a Startup Team
- Founder/CEO: Provides vision, leadership, and strategic direction.
- CTO/CPO: Oversees product development and technology strategy.
- COO: Manages daily operations and ensures efficiency.
- Marketing/Sales Lead: Drives customer acquisition and revenue growth.
- Finance Officer: Handles financial planning, budgeting, and investor relations.
Strategies for Recruiting Top Talent
Recruiting top talent for a startup can be challenging but essential for success. Here are some strategies to attract the best team members:
- Utilize your network and connections for referrals.
- Showcase your company culture and values to attract like-minded individuals.
- Offer competitive compensation packages and opportunities for growth.
- Utilize online platforms and job boards to reach a broader pool of candidates.
Importance of Fostering a Positive Company Culture, Building a Startup Business
Fostering a positive company culture is vital for team morale, productivity, and retention. A strong company culture can attract top talent and create a cohesive team. Here are some tips to foster a positive company culture:
- Lead by example and embody the values you want to promote.
- Encourage open communication and feedback among team members.
- Celebrate achievements and milestones to boost morale.
Tips for Managing and Motivating a Startup Team
Managing and motivating a startup team requires effective leadership and communication. Here are some tips to keep your team engaged and productive:
- Set clear goals and expectations for each team member.
- Provide regular feedback and recognition for good performance.
- Encourage collaboration and teamwork to foster a supportive environment.
- Offer opportunities for professional development and growth within the company.
Developing a Minimum Viable Product (MVP)
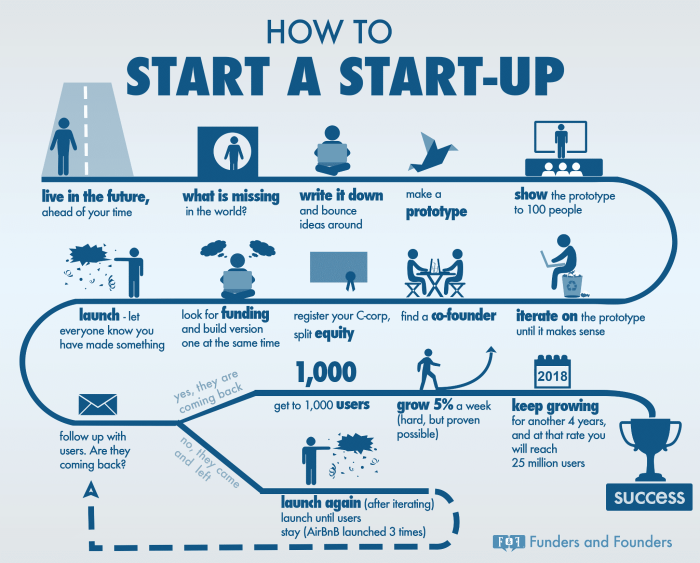
Creating a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) is essential for startups as it allows them to test their business idea with the minimum amount of resources required.
Designing and Testing an MVP
- Identify the core features: Determine the essential features that your product needs to have in order to solve the problem it aims to address.
- Build a prototype: Develop a basic version of your product with the core features to test its functionality and gather feedback.
- Test with early adopters: Get your MVP in the hands of a small group of early adopters to collect valuable insights and improve the product.
- Iterate based on feedback: Use the feedback received from early adopters to make necessary changes and enhancements to the MVP.
Gathering Feedback from Early Adopters
“Your most unhappy customers are your greatest source of learning.” – Bill Gates
- Conduct surveys and interviews: Engage with early adopters through surveys and interviews to understand their needs and preferences.
- Monitor usage patterns: Analyze how early adopters interact with your MVP to identify areas for improvement.
- Track feedback: Keep track of all feedback received and prioritize the most common issues or suggestions for enhancement.
Examples of Successful Companies with MVPs
- Dropbox: Started with a simple MVP that allowed users to store and share files online, leading to its massive success in cloud storage.
- Zappos: Initially, Zappos created a basic website with images from shoe stores to test if people would buy shoes online, paving the way for its e-commerce empire.
- Instagram: Launched with a basic photo-sharing app with filters, which quickly gained popularity and eventually sold to Facebook for billions.